Breathing
Paul has highly realistic upper airways and a physiological lung. This enables the simulation of respiratory pathologies specific to premature babies and the training of all necessary measures under highly realistic conditions.
 |
Normal spontaneous breathing
 |
Once Paul has been switched on and the control software has booted, the simulator starts breathing regularly with a physiological respiratory rate of around 45 breaths per minute and normal lung compliance typical in a preterm of this size.
The respiratory rate can be reduced and increased using the “RR” controller in the monitor area directly to the right of the animated lungs.
NOTE
The rate can be set anywhere between 0 breaths per minute (apnea) and 100 breaths per minute (tachypnea).
The small clock below the respiratory rate slider bar automatically changes the respiratory rate over any defined period of time. The default setting is 5 seconds.
The manikin always breathes at the respiratory rate currently defined and the same respiratory rate is displayed in the 3D animation and the animated lung. When respiration is normal, the chest of the manikin rises and falls and the abdomen also moves slightly, synchronized with every breath.
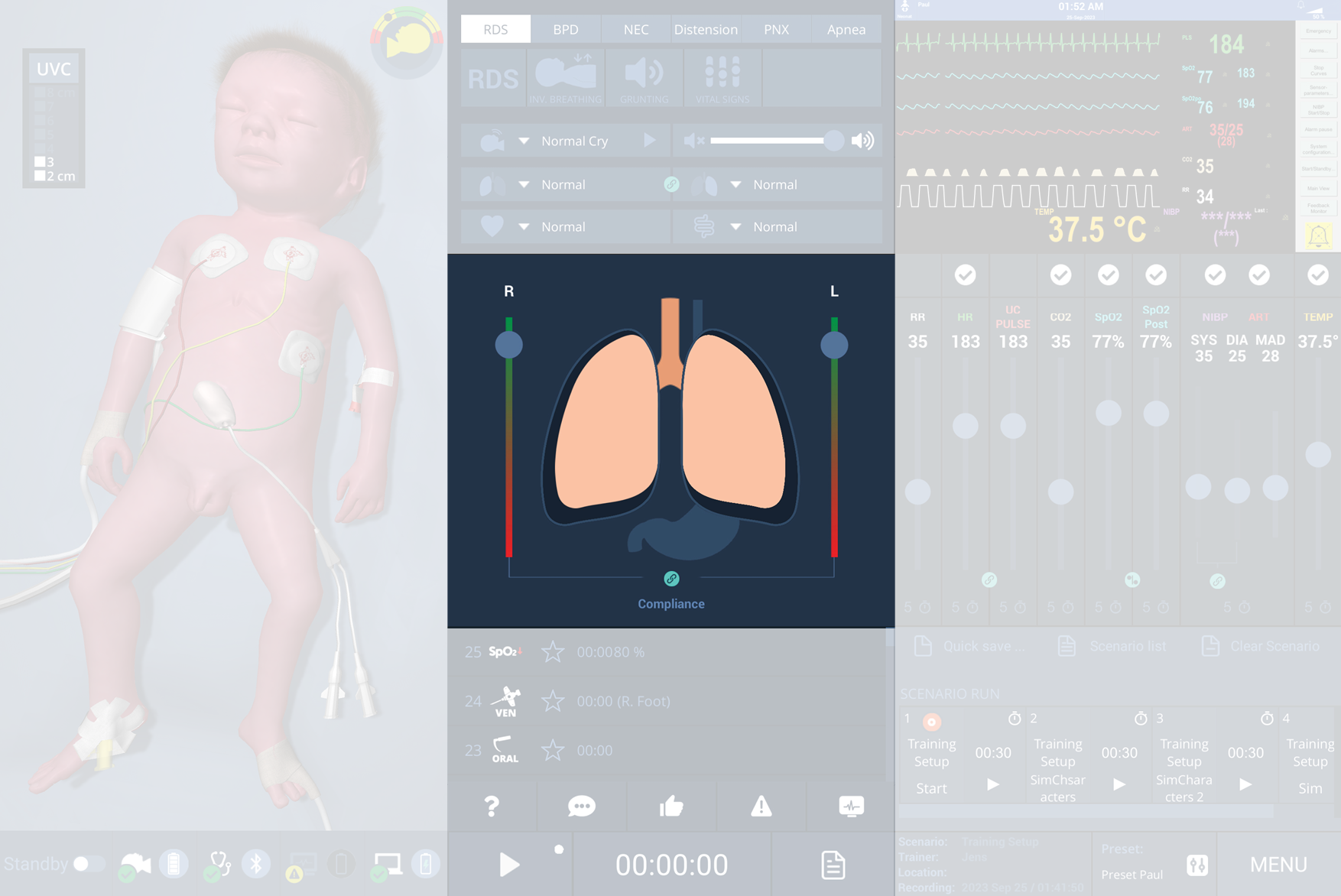
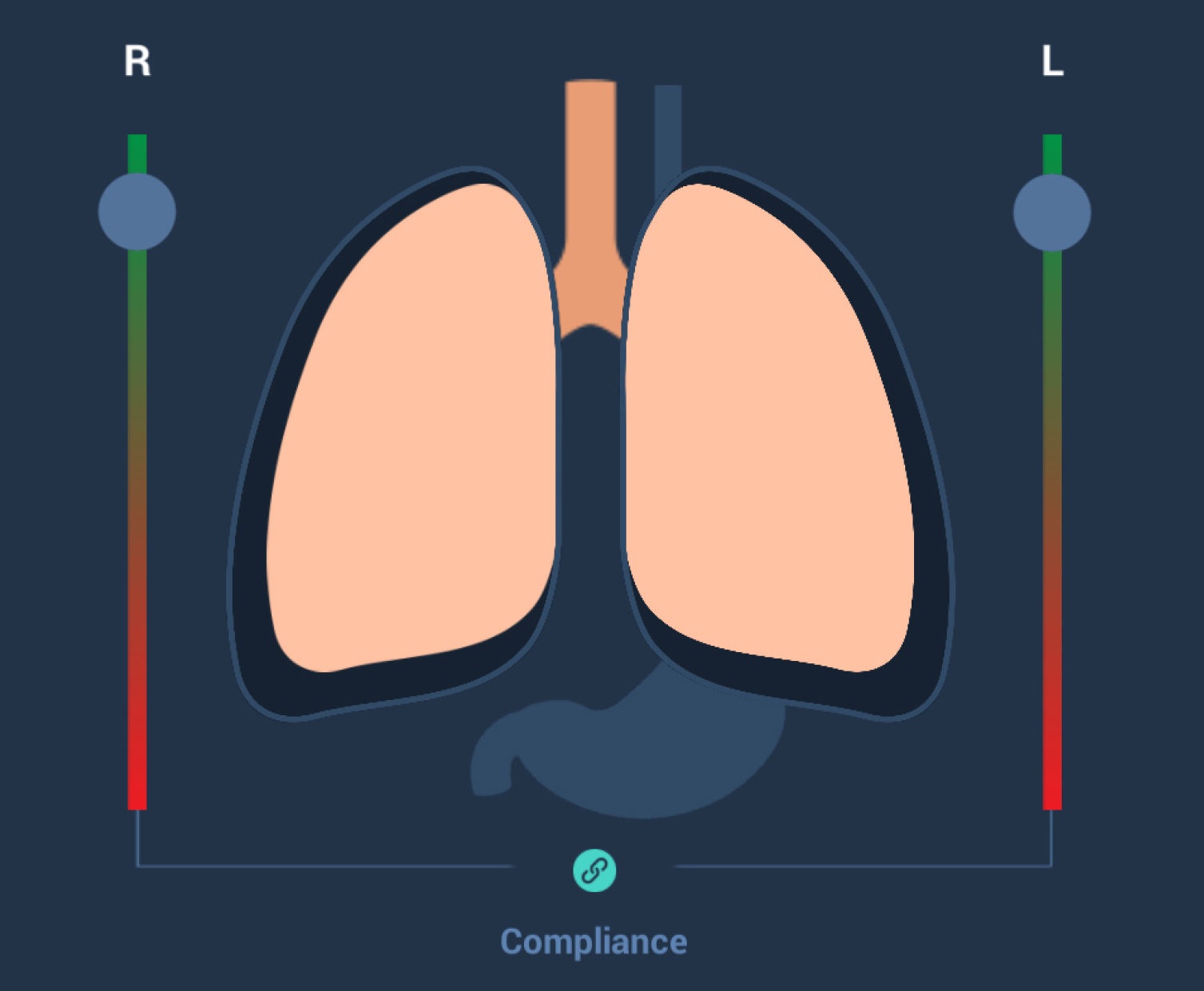
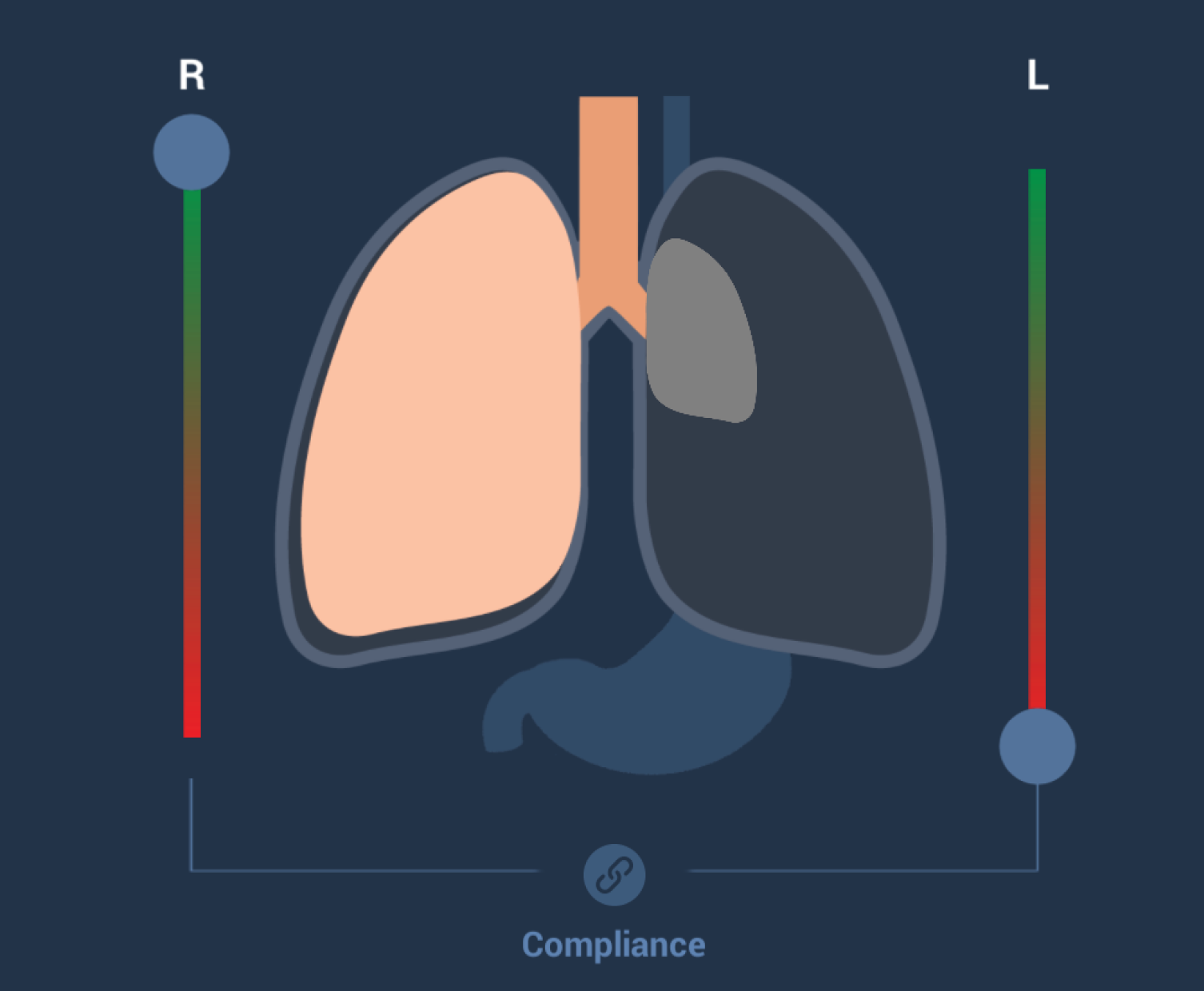
Lung compliance
Paul's physiological lung makes it possible to change lung compliance during a training session using the slider bar directly next to the lung on the GUI.
 |
When the compliance is reduced, the lung volume is also reduced, as a result of which the animated lung becomes smaller and indicates reduced compliance. The manikin is then more difficult to ventilate.
NOTE
For general compliance changes, both lungs must be connected using the “Connect” button, so that the compliance of both lungs changes to the same extent at the same time.
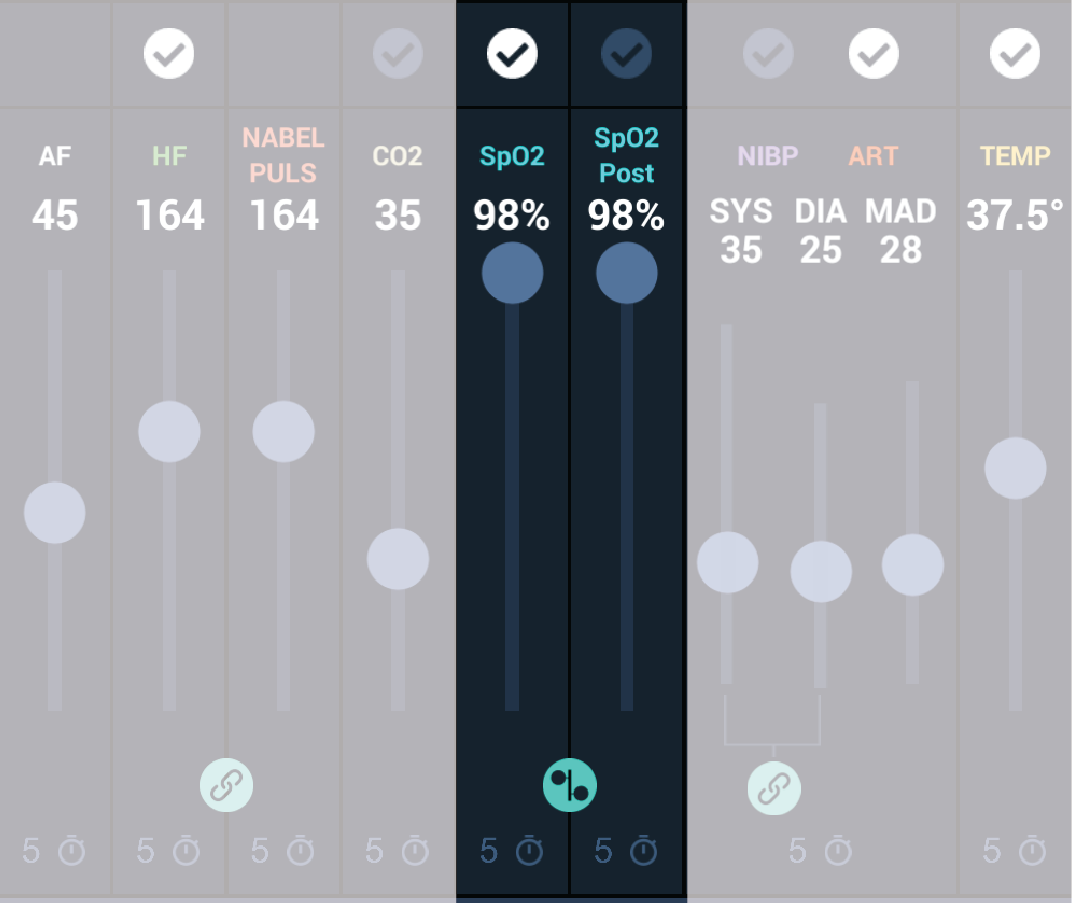
Cyanosis and hyperoxia
The simulator is equipped with multiple LED lights in the head area to visually simulate changes in oxygen saturation.
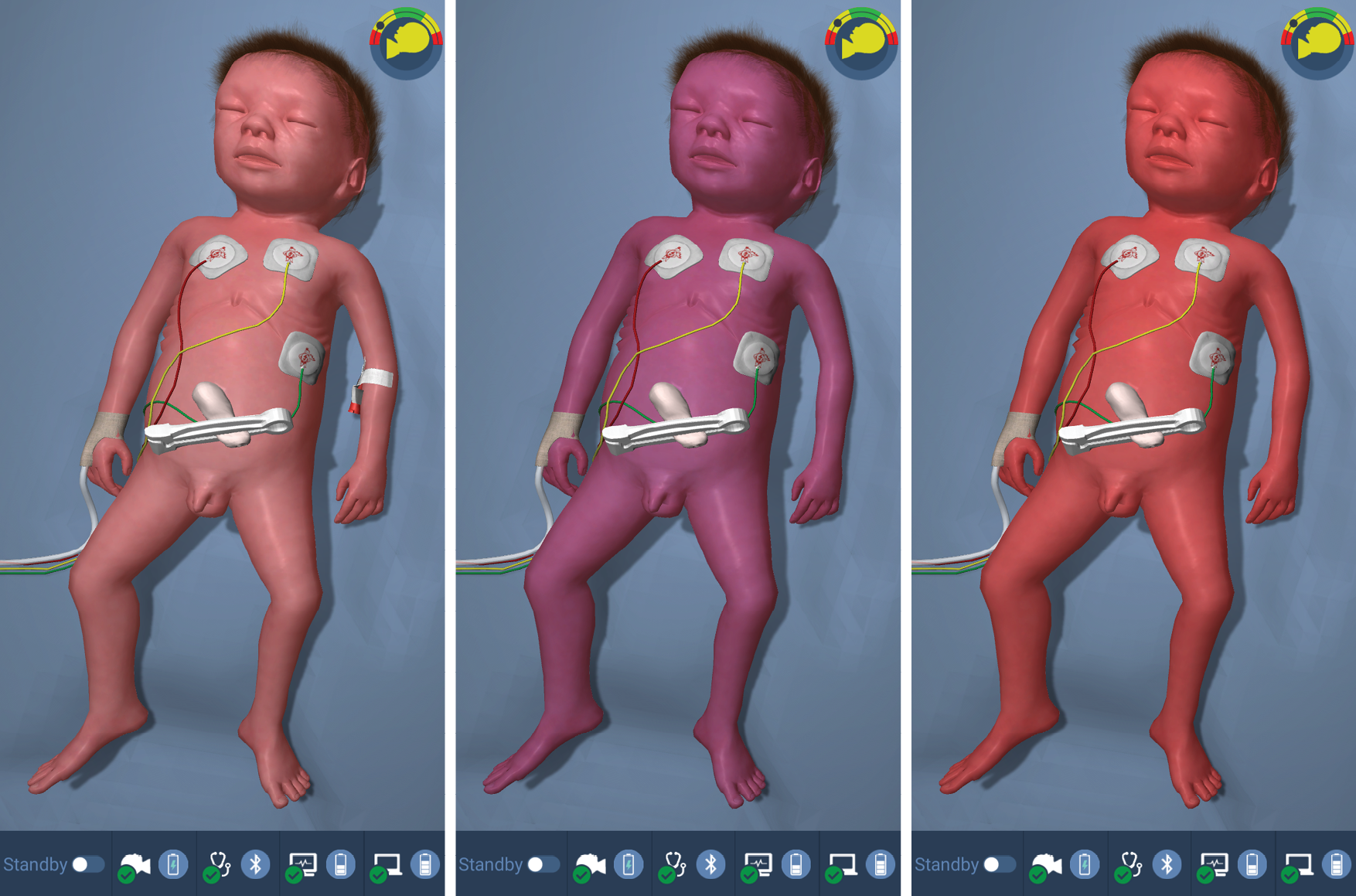 |
Normal saturation: between 97 % and 90 %, the LEDs are in standby mode, with no visible discoloration.
Cyanosis: peripheral saturation below 88 %, a blue discolouration appears in the area of the head, which increases in intensity as the saturation continues to decrease.
Hyperoxia: peripheral saturation above 99%, a red coloration increases in intensity in these areas.
The peripheral saturation (SpO2) can be changed by dragging the slider.
NOTE
The discoloration can be seen both on the simulator and in the 3D animation of Paul on the GUI.
Pneumothorax
Paul allows simulation of a pneumothorax on the right or left (or both) sides.
 |
As a pneumothorax usually occurs unilaterally, it is recommended to cut the link between the two lungs using the "Connect" button to simulate a pneumothorax.
In case of a unilateral pneumothorax, the ventilated side of the chest predominantly rises. On the side of the pneumothorax, only very slight chest elevation or no more chest elevation can be observed. On this side, only weakened or no breath sounds can be auscultated.
CAUTION
The thorax must not be punctured in order to relieve the pneumothorax. This can cause major damage to the technology installed in the chest.