Intraosseous needle placement
Emma/Emily allows for realistic training in intraosseous access placement on both proximal tibias and distal femurs.
The tibia and distal femur are 3D-printed from MRI data of term newborns, reproducing neonatal anatomy for realistic intraosseous access training.
Puncture the skin at the desired site and drill to the optimal position.
Stop drilling as soon as a loss of resistance is felt. This indicates entry into the medullary cavity.
Once an IO access is placed, it can be marked in the Emma/Emily GUI 3D animation using the corresponding input bubbles on the user interface.
The IO placement is then also automatically logged in the debriefing system with a time stamp.
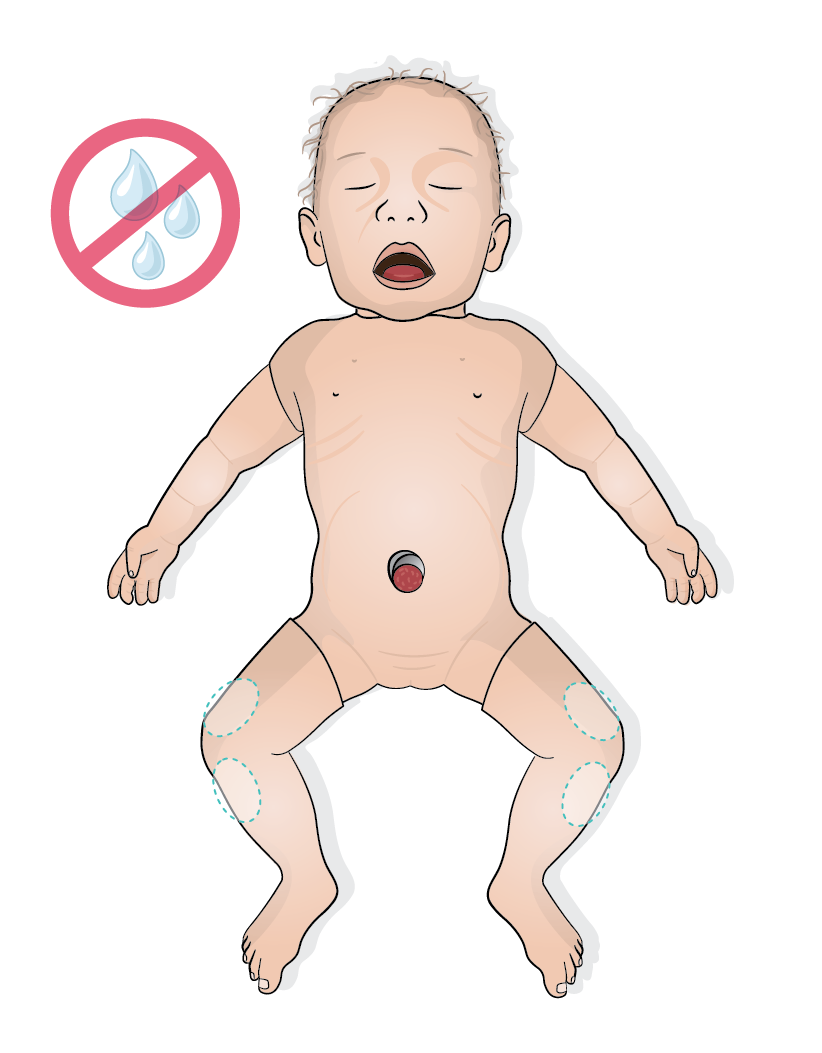
CAUTION
Do not inject drugs or fluids into the IO access in Emma/Emily as this can damage the simulator. Use a bag system with a three-way stopcock for a realistic injection of drugs and fluids. For more information, refer to the Administrating drugs and fluids section.
NOTE
The tibias and femurs are consumable parts, they need to be replaced after multiple drillings. For more information, refer to the Replacing the tibia and Replacing the distal femur section.