Intraosseous needle placement
Emma/Emily allows for realistic training in intraosseous access placement at the following anatomical locations:
Proximal tibia (bilateral)
Distal femur (bilateral)
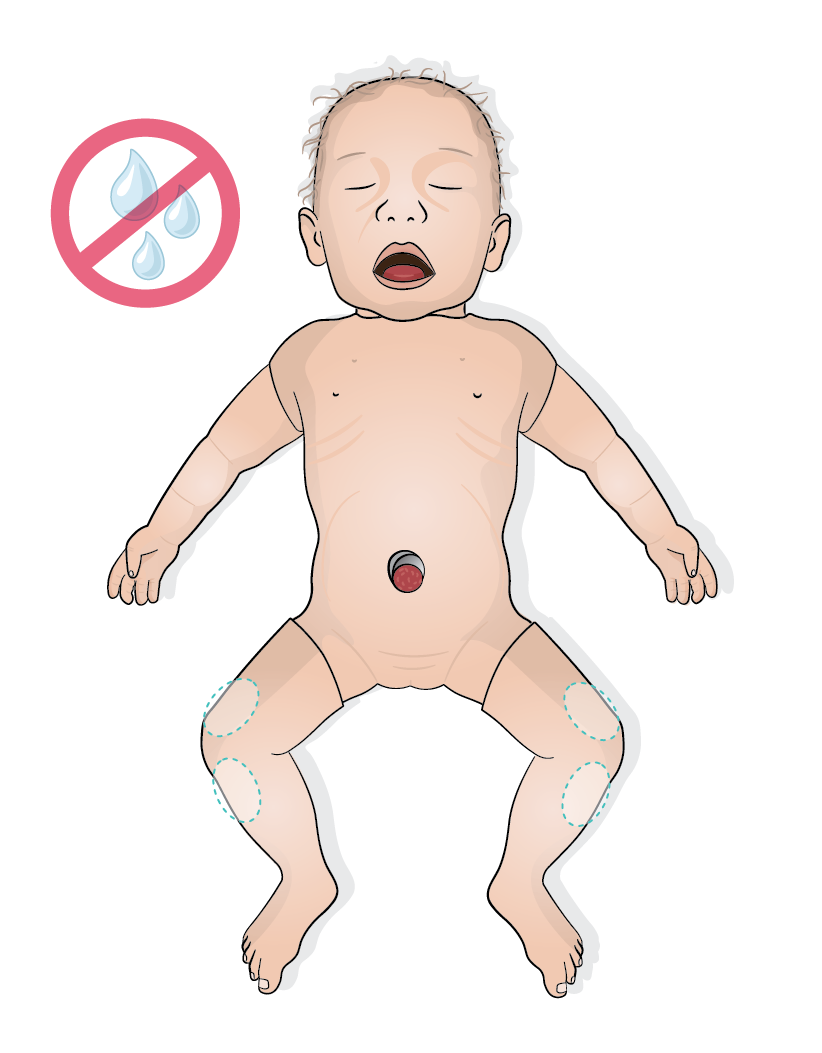
The tibias and distal femurs were developed using 3D printing based on MRI data from real full-term newborns. This ensures highly anatomically accurate structures, allowing for training under highly realistic conditions.
As with a real infant, the skin at the desired location can be punctured, the bone can be felt with the needle, and the optimal position can then be drilled. The drilling process should be stopped once a loss of resistance is felt, replicating the tactile feedback of reaching the medullary cavity in a real patient.
Once an IO access is placed, it can be marked in the Emma/Emily 3D animation using the corresponding input bubbles on the user interface.
The IO placement is then also automatically logged in the debriefing system with a time stamp.
Caution
Never administer any medication or fluids via the IO access, as this may damage the simulator.
For realistic simulation of drug and fluid administration, we recommend using a bag system with a three-way stopcock. This allows for safe and controlled simulation without risking damage to the simulator.
For more information, refer to the Administrating drugs and fluids during simulation scenarios section.